Introduction
One important standard that establishes requirements for stainless steel coils, plates, and sheets is ASTM A240. Stainless steel goods are used in many different industries, such as food processing and aerospace, and ASTM A240 guarantees that they adhere to stringent specifications for surface quality, chemical composition, and mechanical qualities. This standard is essential to the development of contemporary engineering materials because it guarantees their safe and dependable operation in a range of environmental circumstances.
In this article, we’ll look at important grades like UNS S43000, discuss how ASTM A240 affects material selection in contemporary engineering, and dissect the chemical makeup of stainless steel 430, which makes this alloy a popular choice for particular applications. Additionally, we will contrast ASTM A240 type 304 and show how the standard has changed to accommodate contemporary industrial demands.
What is ASTM A240?
Stainless steel sheets, plates, and coils meant for use in high-temperature and corrosive environments are covered by ASTM A240, a specification issued by ASTM International (previously the American Society for Testing and Materials). The standard specifies specifications for austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, and duplex stainless steel grades.
The ASTM A240 specification is essential for ensuring that materials meet industry standards in terms of:
- Chemical composition
- Mechanical properties
- Surface finish
- Formability
For stainless steel goods used in a wide range of industries, such as construction, food manufacturing, and chemical processing, this standard guarantees consistency in manufacturing and quality control.
Key Grades in ASTM A240: UNS S43000
UNS S43000, also known as stainless steel 430, is one of the noteworthy grades under ASTM A240. A ferritic grade of stainless steel, UNS S43000 is renowned for its exceptional resistance to corrosion in mildly corrosive environments, including water and air.
Key Features of UNS S43000:
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent resistance to corrosion from organic acids and atmospheric conditions.
- Magnetic Properties: Unlike austenitic stainless steels like 304, 430 is magnetic, which can be an advantage in certain applications, such as kitchen appliances and automotive exhaust systems.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to austenitic grades like type 304, 430 stainless steel offers good performance at a lower cost.
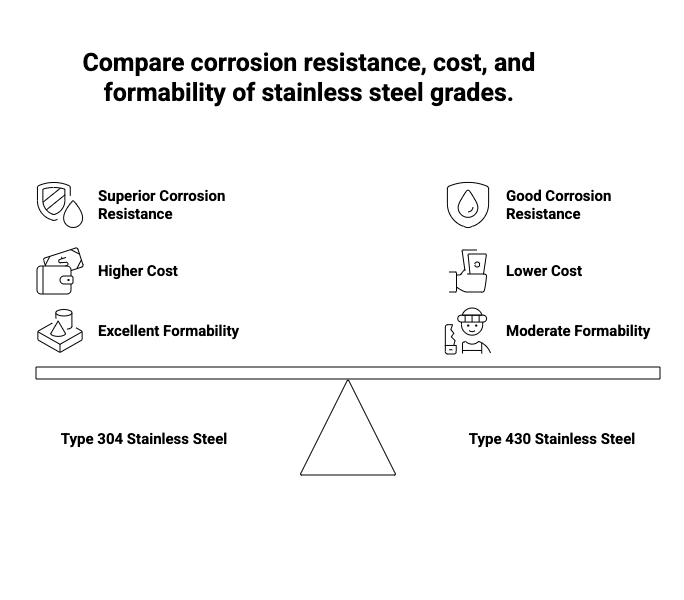
ASTM A240 Type 304: A Comparison
One of the most often used grades of stainless steel is ASTM A240 type 304, particularly for applications needing corrosion resistance and ease of manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Type 304 and Type 430:
- Chemical Composition: Type 304 is more corrosion-resistant, particularly in acidic conditions, due to its greater concentrations of nickel (8% min) and chromium (18%). On the other hand, 430 has less nickel, which lowers both its corrosion resistance and cost.
- Corrosion Resistance: Type 304 is extremely resistant to corrosion in both acidic and alkaline environments and excels at withstanding a broad variety of chemicals. Although Type 430 works well in mildly corrosive situations, it operates badly in surroundings with a lot of chloride or in substances that are extremely acidic.
- Magnetic qualities: For applications where magnetic qualities are unwanted, Type 304’s non-magnetic nature is essential. In contrast, Type 430 is magnetic and frequently used in applications that call for magnetic characteristics.
Applications:
- Type 304 is preferred for kitchen equipment, food processing, and medical devices.
- Type 430 is commonly used for appliances, automotive parts, and architectural applications that don’t require the same level of corrosion resistance as 304.
The Importance of ASTM A240 in Modern Engineering
In order to guarantee that stainless steel products fulfil the exacting requirements for mechanical performance and chemical composition that are necessary in contemporary engineering, ASTM A240 is essential. This specification is essential for the following reasons:
- Consistency and Quality Control: ASTM A240 guarantees that stainless steel plates and sheets meet stringent quality requirements, providing uniform chemical composition and mechanical characteristics.
- Adaptability: The specification is flexible for a variety of applications since it includes a broad range of alloys, such as martensitic, ferritic, and austenitic steels.
- Corrosion Resistance: ASTM A240 guarantees that the materials used are appropriate for the circumstances they will encounter, and many industries rely on stainless steel sheets to avoid corrosion in challenging settings.
- Versatility in Applications: ASTM A240 offers specifications that are appropriate for a variety of industries, including consumer goods, industrial machinery, and architectural design.
The Future of ASTM A240 Materials in Engineering
ASTM A240 materials are changing to satisfy the requirements of more recent applications as industries continue to progress. The future of engineering materials will be shaped by advancements in stainless steel 430 and Monel alloys, as stainless steel becomes more and more important for energy-efficient, sustainable designs.
Because of the emphasis on high-performance alloys and sustainable development, standards like ASTM A240 will keep evolving to meet new demands including rising temperatures, pressures, and more hostile chemical conditions.
Conclusion
In order to shape the stainless steel materials that power modern engineering, ASTM A240 is essential. ASTM A240 guarantees that the material will function as intended even under the most demanding circumstances, whether you choose type 304, stainless steel 430, or Monel 400. Engineers can choose the best material for the work by knowing the chemical makeup of stainless steel 430 and contrasting it with other alloys.
ASTM A240 will continue to be a vital standard for guaranteeing performance, durability, and dependability in a variety of engineering applications due to developments in alloy technology and the ongoing change in industry demands.
FAQ
Type 304 has higher nickel content, making it more corrosion-resistant, while Type 430 has a lower nickel content and is magnetic.
It is widely used in food processing, medical equipment, and construction due to its high corrosion resistance.
Type 430 contains 16–18% chromium and ≤ 0.75% nickel, which gives it moderate corrosion resistance compared to Type 304.
Yes, Type 430 is magnetic, which is useful in certain applications, such as automotive and kitchen appliances.
ASTM A240 covers stainless steel sheets, plates, and coils that are used in a variety of applications requiring high corrosion resistance, such as chemical processing and marine environments.
UNS S43000 is the designation for stainless steel 430, a ferritic alloy that offers moderate corrosion resistance and is used in mild environments.
